Arbitrage is not just a trading method for cryptocurrencies, but there are many ways to employ it in the blockchain ecosystem. However, it’s crucial to understand why these trading possibilities even exist before you pursue crypto arbitrage trading. The notion of crypto arbitrage will be explained in this guide so that, before using it, you are aware of its basic workings. Start with the basics:
What Is Crypto Arbitrage
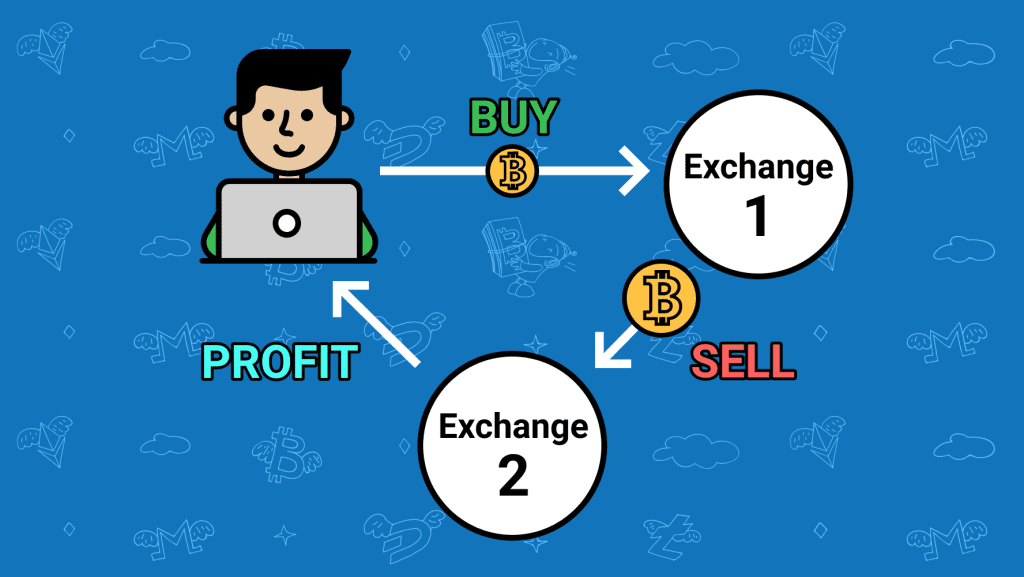
Crypto arbitrage is a trading strategy that aims to take advantage of price differences in crypto currencies. Using the trading method of arbitrage, a trader purchases and sells the same item in other marketplaces in order to benefit from the price disparities between them. The attached images explain this.
- How Does Crypto Arbitrage Function
To begin to comprehend how crypto arbitrage trading operates, you must first be aware that pricing for particular assets on different crypto exchanges such as Trustbity.com may differ slightly, as well as how those values are calculated. Since the price of cryptocurrencies fluctuates often and the market is open around the clock, arbitrage traders want to capitalize on these little price differences in crypto assets.
First, it’s crucial to comprehend how various exchanges set cryptocurrency values in order to comprehend the complexities of crypto arbitrage trading. The fact that not all exchanges determine bitcoin prices in the same way leads to opportunities (pricing differences) between various platforms. Dive in a little more now.
- Centralized Crypto Exchange Pricing (Order Book)
A cryptocurrency asset is valued at its most recent purchase or sale price on centralized exchanges.
Centralized exchanges employ an order book mechanism to set prices. A list of purchase and sell orders for a single asset makes up this order book. You can discover the highest bid and lowest ask pricing at the top of the book. The price of that particular asset on the exchange is then established based on these figures. This is so that a transaction can be conducted promptly at the highest and lowest values, respectively. In essence, order book systems view supply and demand as having complete control over an asset’s price in the market and reacting in realtime to those dynamics.
- Decentralized Crypto Exchange Pricing (Amm)
Decentralized exchanges work through Automated Market Makers, or AMMs, as opposed to order books. What does that signify, though?
A liquidity pool that performs trades with users in accordance with pre-established criteria is an AMM, to put it simply. Users actually engage in trading with the platform’s liquidity pools rather than peers. These liquidity pools work through smart contracts rather than a centralized authority.
What effect does this have on asset values?
In an order book system, users are always given preference over the highest bid and the lowest offer price as the price of assets is decided by the free market. Instead, an AMM analyzes the internal supply of each liquidity pool and how it balances with its trading pair to establish the asset’s price. This indicates that an AMM’s pricing is determined by the demand within its limited ecosystem rather than the movements of the larger market.
- Prices between AMMs and centralized exchanges frequently diverge because assets in an AMM are evaluated by its internal dynamics rather than by the standards of the larger market.
- The potential for crypto arbitrage lies in that disparity.
- Arbitrageurs, incidentally, are crucial to the efficient operation of AMMs. AMM liquidity pools, in essence, depend on these traders to identify pricing inefficiencies and repair them through arbitrage trading.
To be clear, there are other arbitrage opportunities in the crypto ecosystem than trading between AMMs and order book exchanges. However, this is a crypto-specific alternative, making it crucial knowledge for anyone trying to grasp crypto arbitrage.
- Crypto ArbitrageTypes
Crypto arbitrage strategies take a number of different forms, each one taking advantage of price discrepancies across other parts of the market. Here are a couple.
- Triangular Arbitrage
A trading method known as “triangular arbitrage” aims to take advantage of pricing inefficiencies between three different currencies when their exchange rates do not coincide exactly. This could occur inside the same platform or on other exchanges.
Without trading tools, triangular arbitrage opportunities can be challenging to discover. However, these can be pretty well-liked tactics for cryptocurrency arbitrage traders.
- Decentralized Arbitrage
Price variations can exist across centralized exchanges and AMMs as well. Additionally, there are frequent price variations among several decentralized exchanges (DEXs). Decentralized arbitrage is the trading strategy centered on AMMs.
Pricing differences between DEXs are sought after by decentralized arbitrage traders. This has the benefit of costing less than using a centralized exchange, and it also allows traders to maintain complete control of their private keys throughout the transaction. This is due to the lack of support for custodial crypto wallets by decentralized exchanges.
- Risks And Considerations of Cryptocurrency Arbitrage
Arbitrage has considerable risk, just like any other trading approach. It’s crucial to take into account the disadvantages of using these tactics in your trading.
Unfavorable Or Sudden Market Movements
First off, arbitrage trading won’t protect you from the risks associated with unforeseen and bad market situations. If you purchase a token for $100 to sell it for $101 on another platform, but the price of the token abruptly declines, you will not be able to sell it for a profit. Alternatively, the exchange’s pricing could shift, giving the other party the advantage.
Blockchain’s timing inefficiencies can increase the risk in your plan. For instance, the approval time for a blockchain transaction can occasionally be so long that the price has changed.
Legal restrictions are also an option, such as geo-blocking or anti-money laundering checks. For example, while conducting an investigation, an exchange may pause trading for many hours. Alternatively, they might decide not to serve a particular region because of legislative restrictions imposed on or in specific nations.
Platform Charges, Especially on Centralized Exchanges
Arbitrage trading on sites such as Trustbity.com may appear to be quite successful on the surface, but it’s vital to remember that costs typically apply whether withdrawing, putting money into an exchange, or trading cryptocurrency. Given that crypto arbitrage trades take advantage of such minute price variations, it’s crucial to think about how much it might cost you. Some exchangers charge between 1 and 4 percent just to withdraw your own money. Try to keep your exchange fee expenditures to a minimum if you want to maximize your income.
Is Crypto Arbitrage Legal?
Cryptocurrency arbitrage involves exploiting price differences for the same asset across different exchanges. This practice is common in various financial markets, including the cryptocurrency market. However, the legality of crypto arbitrage can be complex and varies by jurisdiction. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Legal Framework:
- Varied Regulations: Different countries have distinct regulations regarding cryptocurrency trading and arbitrage.
- Taxation: In many jurisdictions, profits from crypto arbitrage are subject to taxation, and failure to report such income might be illegal.
- Compliance: Traders must comply with the Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations of the exchanges they use.
Legal Considerations:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that trading activities adhere to local and international laws.
- Reporting Obligations: Adhering to tax obligations and accurately reporting profits and losses.
- Consumer Protection: Ensuring that the arbitrage activities do not manipulate markets or harm other investors.
Risks and Ethical Considerations:
- Market Manipulation: Engaging in activities like pump and dump schemes is illegal in many jurisdictions.
- Insider Trading: Using non-public, material information for trading is illegal.
- Fraud: Engaging in deceptive practices to exploit arbitrage opportunities is unlawful.
Global Perspective:
- United States: The U.S. treats cryptocurrency as property for tax purposes, and arbitrage profits must be reported to the IRS.
- European Union: EU member states have varied regulations, with some treating crypto profits as capital gains.
- Asia: Asian countries like South Korea and Japan have specific regulations and tax structures for cryptocurrency trading.
Legal Challenges:
- Ambiguous Laws: The rapidly evolving nature of cryptocurrency markets often leads to unclear or outdated regulations.
- International Operations: Engaging in arbitrage across borders can subject traders to the laws of multiple countries.
- Privacy Concerns: Adhering to KYC and AML regulations might conflict with privacy considerations in certain jurisdictions.
Future Implications:
- Regulatory Evolution: As the cryptocurrency market matures, regulations are likely to become more defined and standardized.
- Global Coordination: International cooperation might lead to the development of global standards for crypto trading.
- Technological Advancements: The evolution of technology might introduce new forms of arbitrage and associated legal considerations.
- How To Sell Unwanted Gift Card For Cash - March 7, 2024
- Does Circle K Take Google Pay? - January 31, 2024
- Where To Redeem Gift Cards In Nigeria - January 31, 2024